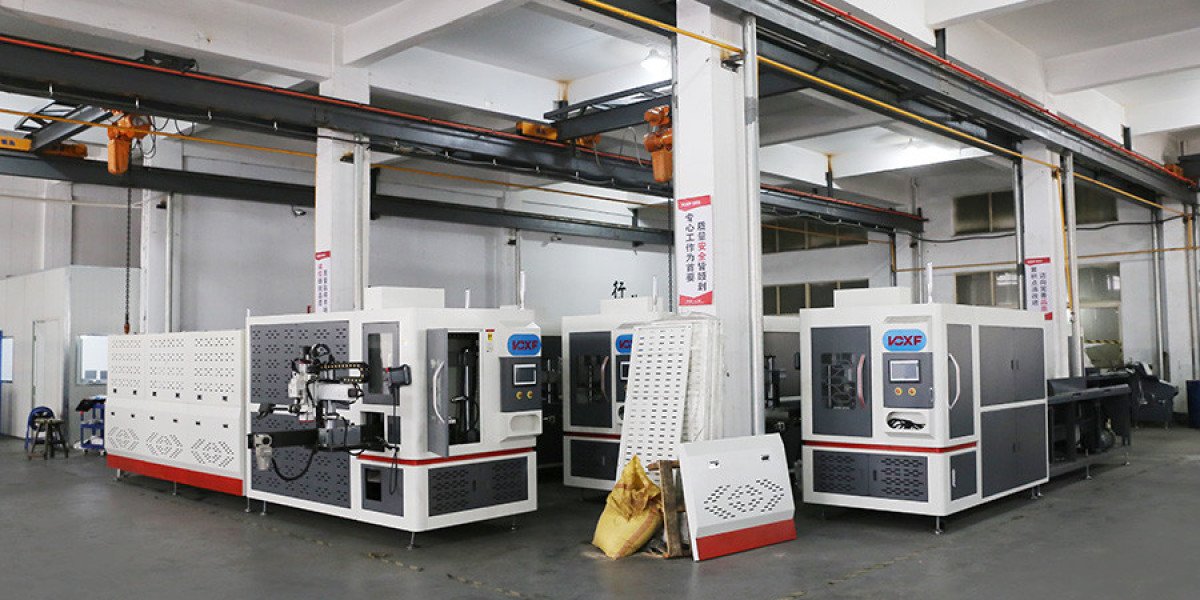
Hot Forging Processing Technology has played a significant role in modern metalworking, offering manufacturers a reliable method to shape metals under controlled heat conditions. By applying high temperatures, metals become more malleable, allowing precise shaping while reducing the likelihood of cracks or defects. The Hot Forging Process ensures that internal grain structures are refined, which improves the mechanical properties of the finished component.
Industries that require durable and strong metal parts, such as automotive and construction, often rely on this process. One of the advantages of using hot forging processing technology is its ability to produce components with consistent quality. The process typically involves heating the metal to a specific temperature range, then applying compressive forces using hammers or presses. This combination of heat and pressure reshapes the metal into the desired form.
Additionally, the hot forging process can accommodate a wide variety of metals, including steel, aluminum, and titanium alloys. Each material responds differently to heat, making it essential for manufacturers to monitor temperature and timing closely. Advances in monitoring and control technologies have allowed modern hot forging processing technology to achieve high repeatability while reducing waste.
Overall, understanding how the hot forging process manipulates metal properties provides insight into why many industries continue to utilize it for critical applications. By controlling heat and deformation, manufacturers can create parts that maintain strength, durability, and functional reliability.